
| Utilities |
| FAQ |
| Links |
| Contact |
| Awards |
| About |
| Creating a real console application in Visual Basic |
Some development tools, like Visual C++ and Delphi, allows the developer to easily create console applications. These tools provides specific methods and functions for writing to the console screen and their compiler also provides special option for creating console executable.
Unfortunately, Visual Basic doesn't support console applications. Even if you use the Win32 API for writing into the console screen,
Your application won't work, because the Visual Basic compiler always creates GUI application and it doesn't provide any compiler options for changing it to console application.
But... with a small trick, it's possible to bypass the limitation of the Visual Basic compiler:
I have developed a small utility that converts an Executable file (.exe) from GUI application mode to console application mode.
So, you can develop a console application in Visual Basic, create an executable file, and then, use my utility to convert the executable into a console application.
My utility was developed in Visual Basic, and the source code is provided within the sample package. You can use it by opening the appmodechange project from Visual Basic IDE.
In order to create a console application in Visual Basic, you have to use Win32 API calls.
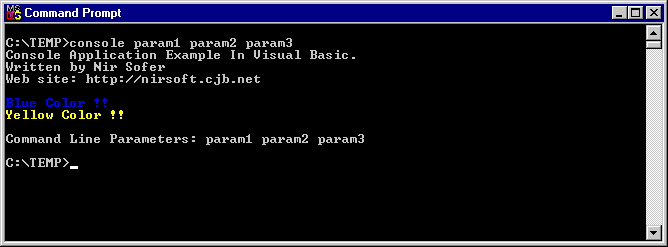
The following code snippet writes a few lines into the console screen, some of them are shown in different colors !
'Console Application Sample 'Written by Nir Sofer. ' 'Web site: http://nirsoft.mirrorz.com ' 'In order to create a console application from this code, follow the instructions below: '1. Make an executable file from this project. '2. Run the "Application Mode Changer" utility and change the mode of the executable file to "Console Application". Public Declare Function GetStdHandle Lib "kernel32" _ (ByVal nStdHandle As Long) As Long Private Declare Function WriteFile Lib "kernel32" _ (ByVal hFile As Long, _ lpBuffer As Any, _ ByVal nNumberOfBytesToWrite As Long, _ lpNumberOfBytesWritten As Long, _ lpOverlapped As Any) As Long Public Const STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE = -11& Private Type COORD x As Integer y As Integer End Type Private Type SMALL_RECT Left As Integer Top As Integer Right As Integer Bottom As Integer End Type Private Type CONSOLE_SCREEN_BUFFER_INFO dwSize As COORD dwCursorPosition As COORD wAttributes As Integer srWindow As SMALL_RECT dwMaximumWindowSize As COORD End Type Private Declare Function GetConsoleScreenBufferInfo Lib "kernel32" _ (ByVal hConsoleOutput As Long, _ lpConsoleScreenBufferInfo As CONSOLE_SCREEN_BUFFER_INFO) As Long Private Declare Function SetConsoleTextAttribute Lib "kernel32" _ (ByVal hConsoleOutput As Long, ByVal wAttributes As Long) As Long Private Const FOREGROUND_BLUE = &H1 ' text color contains blue. Private Const FOREGROUND_GREEN = &H2 ' text color contains green. Private Const FOREGROUND_INTENSITY = &H8 ' text color is intensified. Private Const FOREGROUND_RED = &H4 ' text color contains red. Private hOutput As Long 'The following function writes the content of sText variable into the console window: Private Function WriteToConsole(sText As String) As Boolean Dim lWritten As Long If WriteFile(hOutput, ByVal sText, Len(sText), lWritten, ByVal 0) = 0 Then WriteToConsole = False Else WriteToConsole = True End If End Function Public Sub Main() Dim scrbuf As CONSOLE_SCREEN_BUFFER_INFO 'Get the standard output handle hOutput = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE) GetConsoleScreenBufferInfo hOutput, scrbuf WriteToConsole "Console Application Example In Visual Basic." & vbCrLf WriteToConsole "Written by Nir Sofer" & vbCrLf WriteToConsole "Web site: http://nirsoft.mirrorz.com" & vbCrLf & vbCrLf 'Change the text color to blue SetConsoleTextAttribute hOutput, FOREGROUND_BLUE Or FOREGROUND_INTENSITY WriteToConsole "Blue Color !!" & vbCrLf 'Change the text color to yellow SetConsoleTextAttribute hOutput, FOREGROUND_RED Or _ FOREGROUND_GREEN Or FOREGROUND_INTENSITY WriteToConsole "Yellow Color !!" & vbCrLf 'Restore the previous text attributes. SetConsoleTextAttribute hOutput, scrbuf.wAttributes If Len(Command$) <> 0 Then 'Show the command line parameters: WriteToConsole vbCrLf & "Command Line Parameters: " & Command$ & vbCrLf End If End Sub |
After you create an executable file from this code, you have to use the Application Mode Changer for changing the executable mode from GUI application to console application.
After you convert it to console mode, you'll get the following result:
| Download the projects and executables |
| View the source code of Application Mode Changer |